What is the Law of Supply?
The law of supply is a fundamental economic principle that states: as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers rises. The supply curve depicts this relationship between price and quantity supplied graphically, which slopes upward from left to right.
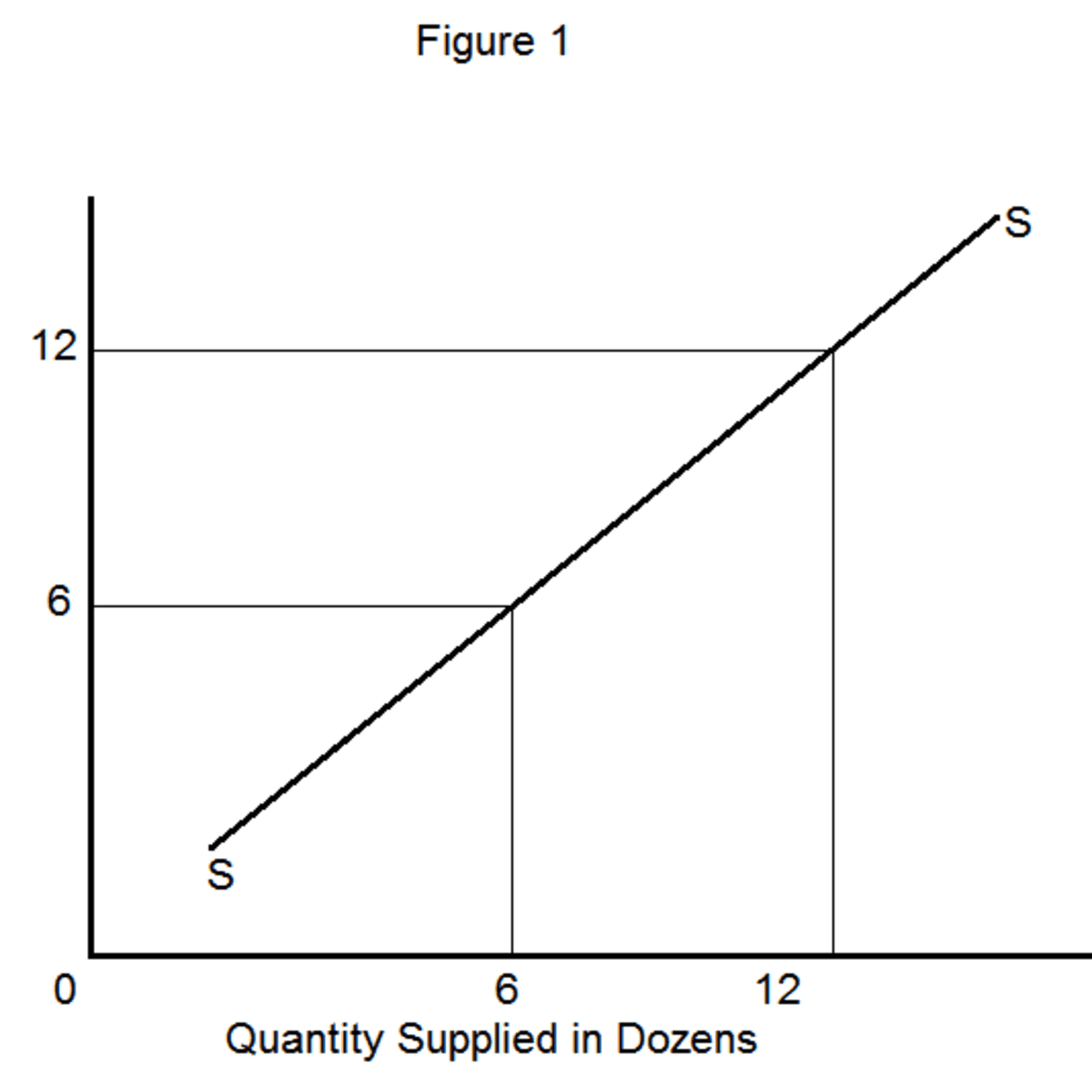
Source: HubPages
Suppliers are motivated to produce more when prices are higher because they can earn greater profits. Conversely, if prices drop, suppliers may reduce production to avoid losses. This concept is crucial in understanding how market supply is determined in an economic system.
One key aspect of the law of supply is that it assumes all other factors influencing supply remain constant. These factors include production costs, technology, and resource prices. Any changes in these variables can lead to shifts in the supply curve.
External factors like natural disasters or government regulations can also impact supply in real-world scenarios. For example, a drought affecting crop yields can reduce the total supply of agricultural products, leading to higher consumer prices.
Understanding the law of supply helps economists predict how suppliers will respond to changes in market conditions, enabling better analysis of production trends and pricing strategies.
Types of Law of Supply
There are five types of laws of supply that govern how businesses respond to changes in price levels. These include:
Market Supply: Refers to the total quantity of a product or service that all suppliers can offer for sale at various prices in a specific market.
Short-Term Supply: Refers to the immediate availability of goods or services in the market based on current production levels and inventory.
Long-Term Supply: Refers to the quantity of goods or services that producers are willing and able to supply over an extended period, typically influenced by factors such as production capacity, technology, and market conditions.
Joint Supply: Refers to a situation where the production of one good results in the simultaneous production of another related good.
Composite Supply: Refers to a situation where multiple goods or services are provided together as a single package.
Additionally, two main supply curves—the individual supply curve and the market supply curve—are commonly used to illustrate these concepts.
The individual supply curve represents the quantity of a good or service that an individual producer can supply at different price levels. In contrast, the market supply curve shows the total quantity supplied by all producers in the market at each price level.
History of the Law of Supply
The Law of Supply has its roots in classical economic theory, dating back to the 19th century. Economist Alfred Marshall first introduced it in his book “Principles of Economics” published in 1890.
This foundational principle helps to explain the relationship between price and quantity supplied in a market economy. Understanding how businesses make production decisions based on market conditions is essential. Over time, the law of supply has become a fundamental concept in economics and is widely taught in introductory economics courses worldwide.
Why is the Law of Supply important in business?

The law of supply plays a crucial role in guiding business decisions. Understanding this law helps companies navigate the complexities of business scenarios by predicting how suppliers will respond to changes in price. Businesses can make informed decisions that maximize potential profits by comprehending the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Competitive Market
In a competitive environment, firms rely on the law of supply to assess how changes in pricing strategies impact their ability to generate revenue. This knowledge enables businesses to adapt to fluctuations in consumer demand and adjust their production levels accordingly. By recognizing the importance of this economic concept, companies can strategically allocate resources to optimize investment and enhance profitability.
Incentive
Moreover, the law of supply serves as a powerful incentive for businesses to increase production when prices rise, leading to higher revenue generation. This understanding empowers organizations to capitalize on market opportunities and stay ahead of competitors. Ultimately, integrating the principles of supply into decision-making processes allows businesses to thrive in dynamic economies.
Equilibrium Price
In the law of supply, equilibrium refers to the point where the quantity of a good or service supplied by producers matches the quantity demanded by consumers. The market is in balance at this equilibrium point, with neither a surplus nor a shortage of goods. Prices are stable, and producers and consumers are satisfied with the market conditions.
If the price is above the equilibrium level, there will be a surplus of goods, leading to a decrease in price. Conversely, if the price is below the equilibrium level, there will be a shortage of goods, causing prices to rise. The law of supply helps to explain how markets reach this equilibrium point and how prices adjust to ensure supply meets demand.
Factors Influencing the Law of Supply
The following factors can impact the law of supply:
- Input prices.
- Production technology.
- Prices of related goods.
- Number of suppliers.
- Expectations of future prices.
What are some examples of how the Law of Supply works in Business?

Here are a few examples of how the law of supply works in business.
Pricing of goods: When the supply of a specific product increases, the price tends to decrease due to the surplus of goods available. Conversely, when the supply decreases, the price typically rises as demand exceeds supply.
Production levels: In response to an increase in demand for a particular product, businesses will often ramp up production to meet the needs of consumers. This demonstrates how the law of supply works by showing that as demand rises, so does the quantity supplied.
Labor market: In industries with a shortage of skilled workers, wages tend to increase as businesses compete to attract and retain employees. This is a direct result of the law of supply, where limited supply (skilled workers) leads to higher prices (wages).
How does the Law of Supply impact the pricing of goods?

The law of supply directly influences how prices are determined for goods. As sellers produce more, the price rises due to increased production costs. Production costs may decrease when technology advances, leading to lower prices for consumers.
Moreover, if production costs increase, sellers are likely to raise their prices to maintain profitability. This is especially evident when inventory-carrying costs are involved in storing goods over time.
In essence, the law of supply impacts not just one item but can affect multiple goods simultaneously. For instance, if the cost of raw materials used in manufacturing various products goes up, the prices of those products will also increase.
Law of Supply Product Pricing Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Helps determine the optimal pricing strategy based on the availability of goods.
- Allows businesses to adjust prices in response to changes in supply.
- Can help prevent overpricing or underpricing of products.
Cons:
- Does not take into account other factors that may influence demand, such as consumer preferences or competition.
- Pricing based solely on supply may not always reflect the true value of a product.
- May lead to price fluctuations if supply is inconsistent.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are the most common questions about the law of supply.
What is the Law of Demand?
The law of demand states that as prices rise, the quantity demanded decreases, showing an inverse relationship. Factors like availability, consumer preferences, and weather affect demand, such as increased demand for ice cream in hot weather.
Businesses rely on demand forecasts to adjust production levels, analyzing trends to meet customer needs. Consumer purchasing power also impacts demand, with higher disposable income leading to increased spending on desired products.
How does the Law of Supply relate to Supply and Demand?
Supply and demand is a fundamental economic principle that describes the relationship between the availability of a good or service (supply) and the desire for that good or service (demand). Prices tend to decrease when supply is high and demand is low. Conversely, prices tend to increase when supply is low and demand is high.
The law of supply is a crucial component of this concept. It states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers also increases. This is because a higher price incentivizes producers to supply more of a product to maximize profits. On the other hand, if the price of a good or service decreases, the quantity supplied by producers will also decrease.
What is the Law of Supply – Final Thoughts

The law of supply is a fundamental economic principle that explains the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied by producers. It helps businesses make more informed decisions in the marketplace. Embracing the law of supply can lead to better resource allocation and overall economic efficiency.
Contact us if you have more questions about small business pricing strategies or to apply for a small business loan. Our alternative financing experts can help you find the best funding option for your business needs.













