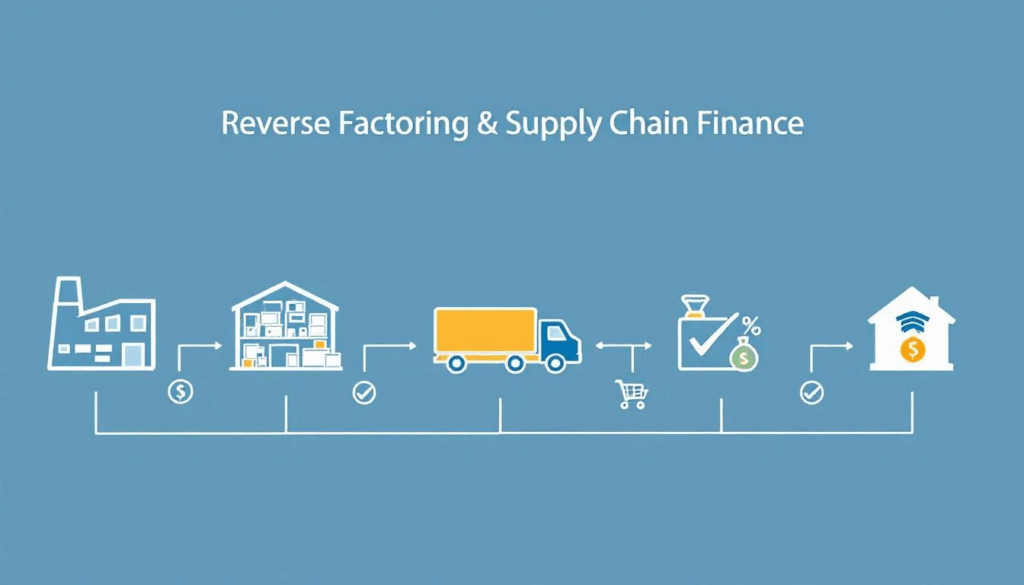
What is Reverse Factoring?
Reverse factoring is an alternative financial arrangement in which a buyer initiates a process that enables smaller suppliers to receive payments quickly, thereby helping them manage their cash flow more effectively. In this reverse factoring arrangement, the buyer enters into an agreement with a third-party financier, such as a bank or specialized financial institution, which pays the supplier’s invoice in advance, providing the supplier with the working capital to complete production and deliver goods to the purchasing company. The buyer then repays the financing company on its scheduled due date, which typically falls within the standard payment terms.
This process supports supply chain resilience and is a form of accounts receivable financing that helps businesses optimize their working capital and ensure liquidity. Reverse factoring empowers small and medium-sized businesses by providing faster payment solutions, thereby improving cash flow and reducing the reliance on high-interest credit lines.
The financing structure helps sustain supply chain production. Reverse factoring is sometimes referred to as Supply Chain Finance, although technically it’s just one component of the broader Supply Chain Finance umbrella.
The supplier’s early payment, which is essentially a cash advance, comes at a discounted rate. The discounted percentage, along with interest payments, is how the financing company makes a profit.
Early payments provide suppliers with the working capital they need to cover their day-to-day expenses. The buyer then has the freedom to wait until the invoice matures or the standard payment terms are met to pay the financier, while ensuring supply chain consistency.
Reverse factoring is considered off-balance sheet financing, as it reduces the amount of debt reported on the buyer’s financial statements. Financial institutions involved in reverse factoring earn income from fees and interest payments charged to the buyer and supplier.
How does Reverse Factoring work?
The reverse factoring process is powered by fintech solutions, enabling the upload of invoices, wire transfers, and invoice payments between the parties involved. The buyer side applies to the financial institution or third-party lender to initiate the financing arrangement.
As part of this process, the buyer or third-party lender can offer early payments to suppliers. The supplier then agrees to the payment terms and discount rate before the reverse factoring transaction takes place, receiving early payment for their invoices.
Reverse Factoring Explained
- The buyer places an order for goods or services.
- The supplier delivers the goods or services on credit and issues an invoice.
- The buyer approves the invoice, and the supplier sends it to the financial institution.
- The financial institution advances funds for the approved trade receivables (invoices) at a discounted rate.
- The buyer pays the financial institution on the invoice due date.
This process helps suppliers better manage their trade receivables and plan for future payments and investments.
Understanding the Supply Chain
The supply chain is the backbone of any business that produces or delivers goods and services. It’s a complex network that connects organizations, people, and processes—from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, logistics, and finally delivering products to the end customer. Effective supply chain management is essential for maintaining a competitive edge, controlling costs, and ensuring timely delivery.
Supply chain finance, including solutions such as reverse factoring, plays a crucial role in keeping this network running smoothly. By optimizing cash flow, businesses can avoid disruptions, pay suppliers promptly, and strengthen supplier relationships. This financial support helps suppliers access the working capital they need to purchase raw materials, maintain production schedules, and meet demand, ultimately benefiting the entire supply chain.
Factoring Companies and Their Role
Factoring companies are specialized financial institutions that help businesses manage their cash flow by advancing funds against outstanding invoices. In the context of reverse factoring, these companies act as intermediaries between buyers and suppliers. Once a buyer approves an invoice, the factoring company steps in to provide early payments to the supplier, often at a discounted rate.
By assessing the buyer’s creditworthiness and managing the risk of the transaction, factoring companies enable suppliers to receive payments earlier than the original payment terms would allow. This improves the supplier’s cash flow situation, reduces the stress of waiting for outstanding invoices to be paid, and enables them to reinvest in their operations. For many businesses, partnering with a factoring company is a practical way to access working capital and maintain financial stability.
What are the benefits of Reverse Factoring?
Reverse factoring involves three parties: the supplier, the buyer, and the financial institution. Financial organizations, such as banks and specialized lenders, also benefit from participating in reverse factoring agreements. This arrangement can help mitigate supply chain risk by ensuring suppliers have access to working capital, which supports the stability and efficiency of the entire supply chain. Let’s examine the benefits of reverse factoring for each one.
Supplier Benefits
Suppliers benefit from reverse factoring because it gives them early access to working capital. Most suppliers are smaller companies that supply the needs of larger companies and corporations.
As a smaller business, suppliers are unlikely to qualify for business financing or only get high rates. With reverse factoring, the financing company bases credit decisions and the interest rate on the buyer’s credit. The financier evaluates the buyer’s credit rating to determine credit risk and set the terms of the agreement. This allows suppliers to access lower-cost financing they might not otherwise qualify for.
Supplier businesses are often still in the growth stage and incur high capital expenditures. Interruptions to cash flow from delayed payments can halt a business in its tracks and may lead to a cash flow crunch. Financial institutions generally consider larger companies as lower credit risks when entering financing arrangements.
Reverse factoring enables consistent early payments on invoices, ensuring smooth operations and maintaining sufficient funds to cover day-to-day expenses. It also strengthens the relationship with the buyer.
Benefits for the Buyer
The buyer has more time to pay the invoice, helping with cash flow management. Providing funding to suppliers ensures they have the necessary cash to meet deadlines and keep the supply chain moving.
Reverse factoring also helps strengthen the relationship with the supplier. In addition, many suppliers offer an early payment discount, which is a percentage reduction on the invoice amount as an incentive for buyers to pay invoices before the due date. Reverse factoring enables buyers to benefit from the early payment discount while still waiting to settle the invoice at maturity.
Suppliers often find it challenging to access affordable funding solutions without assistance from larger buyers. Large corporations usually have better creditworthiness than smaller suppliers, making it easier for them to secure financing.
Benefits for Financial Institutions
Reverse factoring offers a steady revenue stream for financial institutions, including factoring companies, banks, and other alternative business lenders.
What are the drawbacks of Reverse Factoring?
While reverse factoring programs offer numerous benefits, they also have some downsides. For the supplier, the most obvious downside is the discounted rate. Suppliers must decide whether the early payment justifies accepting less money than what is owed.
The buyer initiates reverse factoring, and the supplier decides whether to accept or not. The drawback for the supplier is that it can’t initiate the financing agreement. The buyer faces the possibility that the supplier rejects the agreement in favor of other arrangements, such as factoring their receivables.
Most factoring companies, banks, or other institutions only agree to reverse factoring when the buyer and supplier have a long-standing relationship. Additionally, reverse factoring contracts often span a lengthy period, resulting in a significant commitment for all parties.
Reverse factoring is a lesser-known financing strategy compared to traditional factoring arrangements, and it depends on fintech solutions. As such, companies have limited choices of lenders that provide reverse factoring arrangements.
Different states and countries have regulatory guidelines that hinder reverse factoring. Ensure you look into the financing laws governing your state or country.
Reverse Factoring Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Provides early payments & working capital to suppliers.
- Provides suppliers with lower-cost funding.
- Suppliers leverage the buyer’s credit for approval.
- It gives buyers more time to pay their invoices.
- Helps strengthen the buyer-supplier business relationship.
- It helps ensure the supply chain moves smoothly.
Cons:
- Discount rates eat into the suppliers’ profit.
- Reverse factoring agreements are long contracts.
- Suppliers & buyers need to have a long-standing relationship.
- Suppliers may reject factoring as part of their own funding arrangement.
- Dependent on fintech and a lesser-known financing program.
- Potentially limited by state and country regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the most common questions about reverse factoring.
What’s the difference between Reverse Factoring and Invoice Factoring?
When comparing reverse factoring and invoice factoring, it is essential to understand the key differences between these two financial strategies.
Invoice factoring allows businesses to sell their accounts receivable directly to a factoring company, or Factor, in exchange for a cash advance. The Factor then owns the invoice and collects payment from the buyer.
In the Reverse process, the buyer initiates the factoring agreement and works directly with the Factor. The buyer still pays the factoring company in a reverse factoring program. The buyer benefits from reverse factoring by extending payment terms without having to negotiate other factors.
With invoice factoring, approval typically depends on your customers’ credit rating. Approval for reverse factoring depends on the buyer’s credit rating.
The supplier sells its accounts receivable to the financing partner at a discount in traditional factoring. In traditional factoring, the supplier is responsible for selling their invoices to a third party.
Is Reverse Factoring the same as Dynamic Discounting?
There are similarities between the two, but reverse factoring and dynamic discounting are separate programs. In reverse factoring, a third-party financing company provides funding to the supplier for early payment. In dynamic discounting, the purchasing company deploys its own capital to fund the early payment.
Dynamic discounting continues to provide suppliers with working capital, enabling them to keep their businesses running. The buyer benefits from the discounted sales price and avoids supply chain interruptions, but has to provide the money upfront.
Which industries use Reverse Factoring?
Reverse factoring is available for most business-to-business (B2B) companies that purchase on credit. The industries that use reverse factoring most often are:
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Clothing
- Electronics
- Manufacturing
How common is Reverse Factoring?
Despite its numerous benefits, reverse factoring remains a relatively uncommon and lesser-known financing method. It’s estimated that reverse factoring only accounts for 3% of the factoring market. Reverse factoring has seen increased popularity due to the uncertainty in global supply chains after the pandemic.
Reverse factoring began in the automotive industry during the 1980s. Car makers sought to strengthen supply chains by providing suppliers with capital to keep their businesses running.
It has made its way into the retail industry, as payment delays are common in this sector. Reverse factoring remained a niche solution for these industries until fintech capabilities and platforms experienced significant growth over the last decade.
The most significant area for growth in reverse factoring is in the global marketplace. Globalization and offshore production resulted in an expansion of the supply chain. Many businesses experienced a reduction in available capital as a result.
The shifts in the global supply chain created a need for Global Supply Chain Finance (GSCF). While reverse factoring helps provide working capital for businesses in the global supply chain, the laws impacting different countries make it difficult to implement.
However, industry benchmarks suggest that GSCF programs will likely expand to meet the growing demand for global trade finance. Reverse factoring is likely to continue growing in tandem with the increasing demand for supply chain finance solutions.
Can I apply for Reverse Factoring?
The purchasing company, or buyer, initiates reverse factoring. Suppliers cannot apply for reverse factoring, but they can choose to accept or decline it when a buyer initiates the process.
Buyers are typically large companies or corporations that purchase from various suppliers, which are often small or medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
SMBs rarely possess the same credit and negotiating power as larger purchasing companies. Reverse factoring enables SMBs to tap into the credit of larger companies, securing rates they might not otherwise qualify for.
If you are a small business owner looking to factor your receivables, you can still apply for regular invoice factoring. Invoice factoring is the most common factoring service, providing you with the power to convert unpaid invoices into working capital.
What is Supply Chain Finance?
Supply chain finance enhances the cash flow of buyers and sellers by utilizing a third-party financial institution to finance supplier invoices. A supply chain is a network of interconnected buyers and sellers that depend on each other for success.
Suppliers must manage cash flow forecasting to prevent potential cash shortages in their operations. Cash forecasting is crucial for suppliers to plan liquidity needs and optimize working capital, especially when integrated with ERP systems for more accurate predictions. Effective supply chain management is essential for achieving broader business objectives and cost efficiency.
A strong balance sheet can enhance a buyer’s financial health and make it more attractive to other suppliers and investors. Supply chain finance is often seen as an off-balance sheet solution that can improve financial metrics.
What are my other financing options?
Factoring is a form of working capital financing. If neither invoice factoring nor reverse factoring works for your business, there are several loan options to secure working capital.
Working Capital Loans
There are several forms of working capital loans that provide cash to cover business expenses. Various short-term and long-term working capital loans help your business meet expenses and stabilize cash flow.
Merchant Cash Advance
A merchant cash advance provides an influx of working capital based on a company’s average credit card sales. The business then repays the advance with a percentage of future credit or debit card sales.
Business Lines of Credit
A business line of credit provides a business with funding as needed. It’s like a credit card, where the company is given a set credit limit and can draw funds to cover its cash flow needs. And speaking of business credit cards, you can also look into the Brex Corporate Card to help with business expenses.
Revenue-Based Loan
Revenue based financing provides businesses with working capital and flexible payment terms, allowing them to manage their cash flow effectively. The company’s revenue determines the loan amount. The company then repays the loan with a percentage of future revenue. It’s excellent for businesses with inconsistent revenue streams since the payment fluctuates with revenue.
Other Small Business Loans
Businesses looking for long-term loans with higher borrowing amounts can look into the following:
Reverse Factoring – Final Thoughts
Reverse factoring offers benefits to both suppliers and buyers in the supply chain. However, its biggest drawback is that suppliers, usually small businesses, can’t apply for it. The buyer initiates the factoring process, which is why it is the reverse of standard invoice factoring.
When implemented successfully, reverse factoring helps secure the supply chain and keep all parties’ businesses moving. It’s one of several forms of supply chain finance, although sometimes the term is used interchangeably with reverse factoring.
Globalization has created a growing need for supply chain financing. Expect reverse factoring and other supply chain finance programs to grow in the coming years.
Whether you’re a buyer interested in reverse factoring or a supplier seeking accounts receivable factoring, please get in touch with us to discuss your options. One of our loan experts will discuss your business needs and recommend the ideal financing program to achieve your goals.